Note
Click here to download the full example code
Concentration of the eigenvalues¶
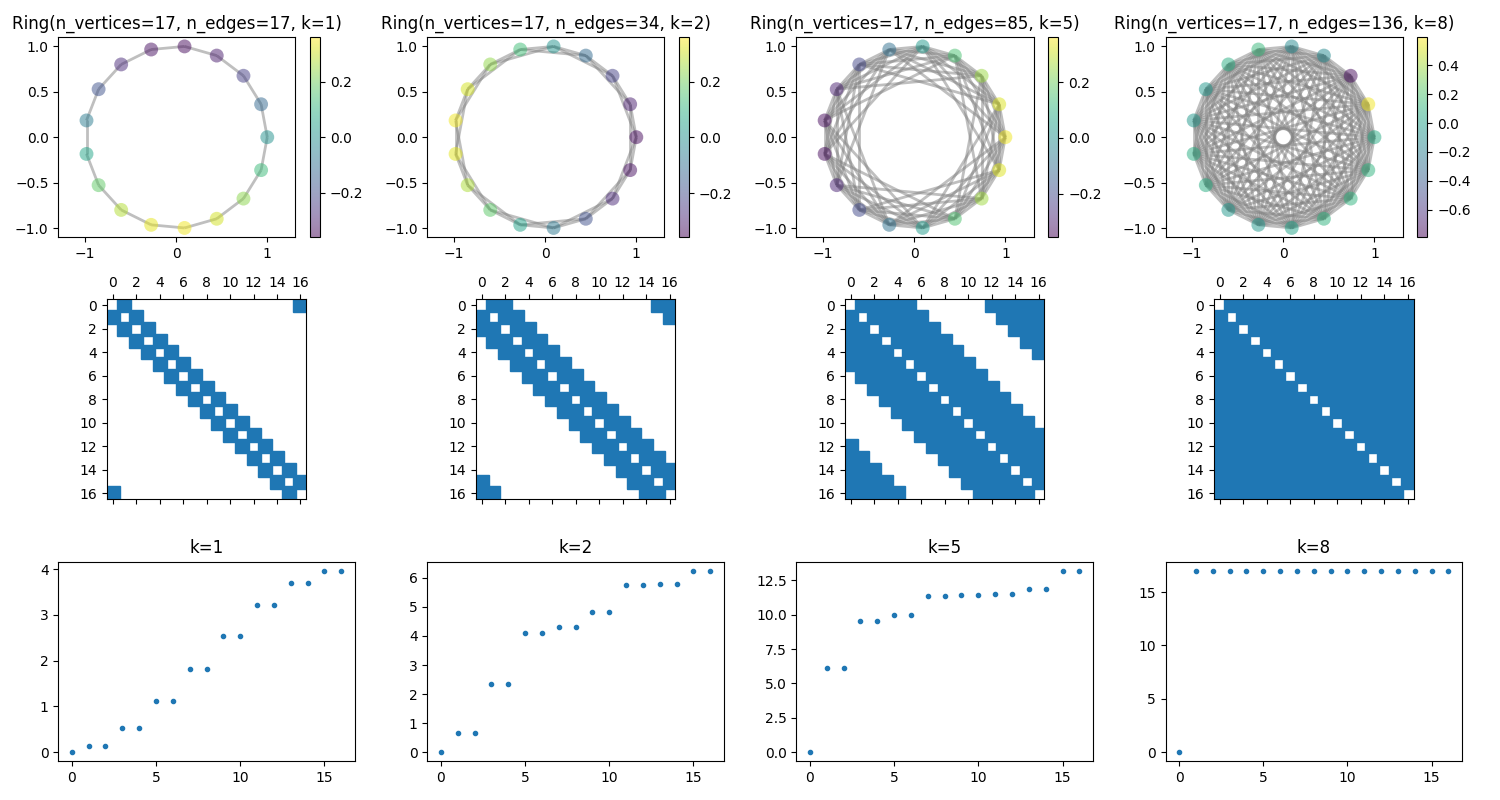
The eigenvalues of the graph Laplacian concentrates to the same value as the graph becomes full.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pygsp as pg
n_neighbors = [1, 2, 5, 8]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, len(n_neighbors), figsize=(15, 8))
for k, ax in zip(n_neighbors, axes.T):
graph = pg.graphs.Ring(17, k=k)
graph.compute_fourier_basis()
graph.plot(graph.U[:, 1], ax=ax[0])
ax[0].axis('equal')
ax[1].spy(graph.W)
ax[2].plot(graph.e, '.')
ax[2].set_title('k={}'.format(k))
#graph.set_coordinates('line1D')
#graph.plot(graph.U[:, :4], ax=ax[3], title='')
# Check that the DFT matrix is an eigenbasis of the Laplacian.
U = np.fft.fft(np.identity(graph.n_vertices))
LambdaM = (graph.L.todense().dot(U)) / (U + 1e-15)
# Eigenvalues should be real.
assert np.all(np.abs(np.imag(LambdaM)) < 1e-10)
LambdaM = np.real(LambdaM)
# Check that the eigenvectors are really eigenvectors of the laplacian.
Lambda = np.mean(LambdaM, axis=0)
assert np.all(np.abs(LambdaM - Lambda) < 1e-10)
fig.tight_layout()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.414 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 14 MB